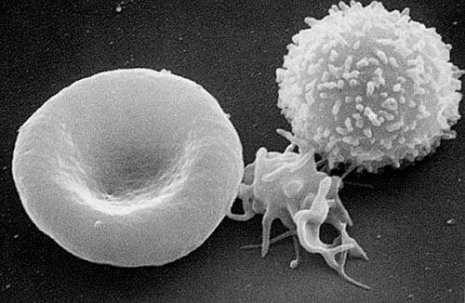
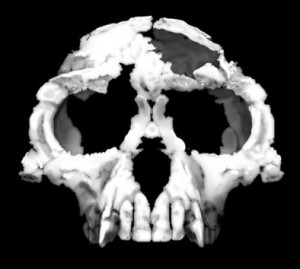
In my previous post, I discussed the proper way to apply the Second Law of Thermodynamics to a simple process: the freezing of water in a bucket. Now I want to apply the Second Law of Thermodynamics to the process of evolution. This is a difficult thing to do, because currently, there is no accepted mechanism for the process of evolution. Evolution might occur according to the Neo-Darwinian Synthesis; it might occur via punctuated equilibrium; it might occur according to the evo-devo view; it might occur as a result of facilitated variation; it might occur by some as yet undiscovered mechanism; or it might occur as a result of a combination of all or some of these mechanisms.
Even though there is no agreed-upon mechanism for evolution, some general statements can be made about the supposed process, and that should be enough to allow us to roughly apply the Second Law of Thermodynamics to it. In general, evolution says that organisms increase in complexity over time. A single-celled organism, for example, eventually developed the ability (through some as yet unknown process) to cooperate with other cells, which eventually led to a multicelled organism. Clearly, a multicelled organism is more complex than a single-celled organism, so via that unknown process, “simpler” single-celled organisms gave rise to “more complex” multicelled organisms. These multicelled organisms began to develop (once again, through some as yet unknown process) more “advanced” features, so that eventually a large diversity of life formed.
The longer evolution had to work through its unknown process, the more complex living creatures became. Thus, while it took some time for the evolutionary process to create relatively “simple” multicelled creatures, it took more time for evolution to produce complex invertebrates, and it took more time for evolution to produce vertebrates. The more “advanced” the vertebrate, the longer it took for evolution to produce it.