Naturalistic evolutionists are forced to look at the world very simply. After all, they think there is no plan or design in nature. Instead, they believe that random events filtered by natural selection are responsible for all the marvels we see today. Because of this unscientific way of thinking, they tend to look for simple processes to explain amazingly complex interactions in nature. Cellular communication is a perfect example of how this simplistic way of looking at things can produce serious errors.
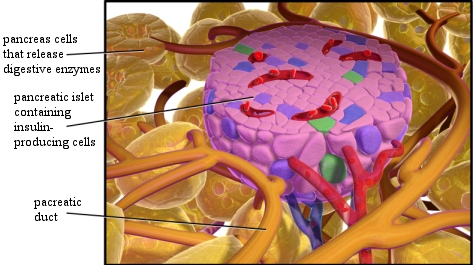
In order for the different cells of an organism to be able to work together, they must communicate with one another. One of the most well-studied versions of cellular communication is called endocrine communication, and the insulin-producing cells in the islets of the pancreas (illustrated above) provide an example of how it works. These cells produce insulin, which is then released into the bloodstream. When cells in the liver, skeletal muscles, and fat tissues are exposed to this chemical, they absorb glucose (a simple sugar) from the blood. By controlling the release of insulin from the pancreatic islets, then, the body can control how much glucose is in the blood.
Now, of course, this is a great design for cellular communication that needs to affect a wide array of cells in many different places. It makes the release of the chemicals easy to control but their effect long-ranging. As a result, when the body needs widespread communication in different cells, endocrine communication is used. However, there are often times when cells need to communicate with other cells that are nearby. This is called paracrine communication, and biologists have taught (as fact) for many, many years that paracrine communication happens in essentially the same way as endocrine communication. For example, one of the volumes of the Handbook of Cell Signaling says:1
Paracrine interactions induce signaling activities that occur from cell to cell within a given tissue or organ, rather than through the general circulation. This takes place as locally produced hormones or other small signaling molecules exit their cell of origin, and then, by diffusion or local circulation, act only regionally on other cells of a different type within that tissue. (emphasis mine)
In other words, a cell releases some signaling chemicals, and those chemicals simply have to find their way to their targets via diffusion or some other local means of movement. Of course, such a signalling scheme is rather inefficient for communication with nearby cells, and new research indicates that it’s not the way paracrine communication is done.
Continue reading “Cellular Communication – Another “Truth” Destroyed”