Will Rogers once said, “The short memories of the American voters is what keeps our politicians in office.” The High Priests of Science are well aware of the public’s short memory. In fact, they count on it. Consider, for example, the picture above. It was a common sight 10-15 years ago. The credulous costumed characters in the picture were terribly worried about the plight of polar bears, which they believed were being driven to extinction because climate change (aka global warming) was melting all the ice in the Arctic. Without that ice, the polar bears would have no habitat, and they would all die.
Why don’t we see lots of protests featuring polar bears anymore? Because even the High Priests of Science can no longer deny the fact that polar bears are thriving. Studies show that polar bear populations have more than doubled since 1960. It turns out that polar bears were on the decline because of hunting, not climate change. Now that the hunting of polar bears has been heavily regulated, the animals are once again healthy and plentiful. The High Priests of Science are counting on you to forget their false statements regarding polar bears and climate change/global warming so that they can continue to promote their propaganda.
Now remember, the polar bears were supposedly threatened by the loss of sea ice in the Arctic. The High Priests of Science have continually predicted that the Arctic would eventually be ice free in the summer. In 2008, for example, Dr. James Hansen told the U.S. Congress that in 5-10 years, the Arctic would be ice-free in the summer. Well, it has been 16 years since his testimony, and there is still a lot of ice in the Arctic, even in the summer. Other scientists have predicted ice-free Arctic summers by 2015, 2013, and 2012. The High Priests hope you have forgotten those predictions now that they claim it will happen by 2030, or perhaps 2067.
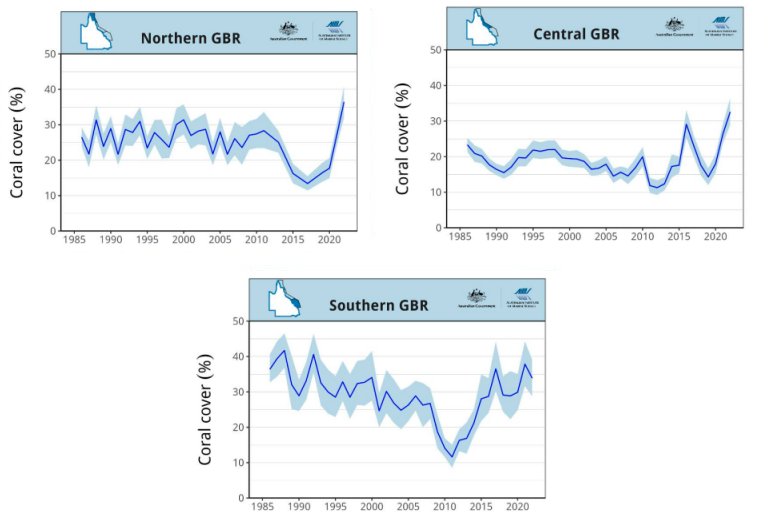
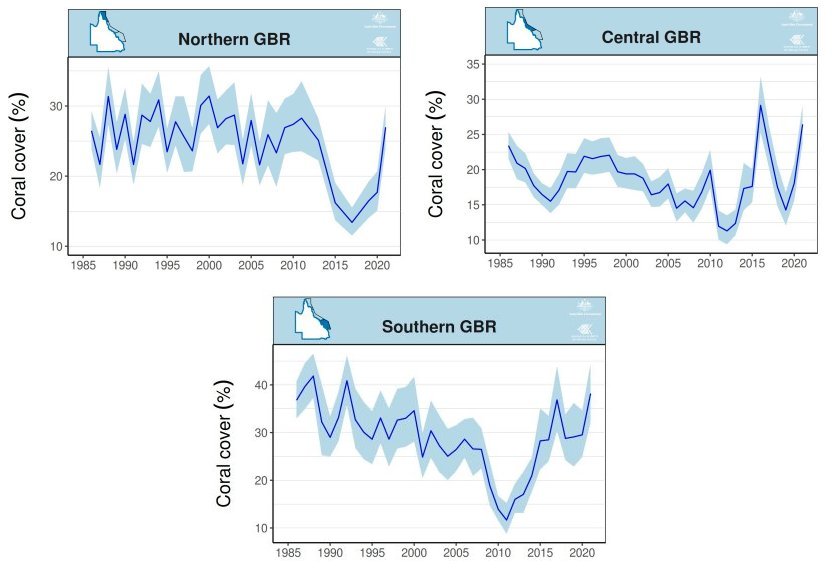
Of course, those aren’t the only things the High Priests are hoping you’ve forgotten. The Great Barrier Reef is another. In 2012, a study predicted that if we did not reduce our greenhouse gas emissions, the central and southern regions of the Great Barrier Reef would see such a decline that only 5-10% would be covered with coral. Two years later, The Guardian published an obituary for the reef. Ten years later, however, the amount of coral in the northern and central regions of the Great Barrier Reef is at an all-time high, and the southern region is very close to an all-time high. Once again, the High Priests of Science hope you will forget about those predictions.
And then, of course, there is sea level. Sea levels have been rising steadily since the mid 1800s, because that is when the earth started recovering from The Little Ice Age, a time when the earth was unusually cold. Despite the fact that at least a large portion of the rise in sea levels seems to be a result of natural fluctuations in the earth’s temperature, the High Priests of Science have predicted that climate change will accelerate it, leading to all sorts of catastrophes. The East Coast’s beaches were supposed to be gone by 2020, the Maldives were supposed to be underwater by 2018, and New York and Washington were supposed to be covered by the ocean in the year 2000. Of course, none of that happened, but the High Priests are counting on you to forget those predictions so they can make new ones.
The next time you hear a dire prediction about what will happen because of climate change/global warming, remember that those High Priests of Science have been making such predictions for a very long time, and they are constantly being proven wrong.