Those who want to believe that dinosaur fossils are millions of years old are faced with two very difficult challenges. First, carbon-14 has been detected in significant quantities in all dinosaur bones that were tested for it. This is a problem, as carbon-14 should decay to unmeasurable levels in about 60,000 years. Second, soft tissue and biomolecules have been found in many dinosaur fossils (see here, here, here, and here, for example), and at least according to some paleontologists, it is a common feature of the fossils. Of course, there is no known way that soft tissue and biomolecules can withstand decay over millions of years, so fervent old-earth scientists have been trying to find one.
Dr. Mary Schweitzer, who was the first to find soft tissue in a dinosaur fossil, proposed a possible explanation more than 10 years ago. Based on an experiment that lasted two years, she and her colleagues proposed that iron from the dinosaur’s blood could have acted as a preservative for the soft tissue and the biomolecules that comprise it. As you can read in the post I linked, I was initially very skeptical of such an explanation. Two years later, two chemists who are much more knowledgeable than I am gave what I consider to be definitive arguments as to why iron cannot do what Schweitzer and her colleagues want it to do.
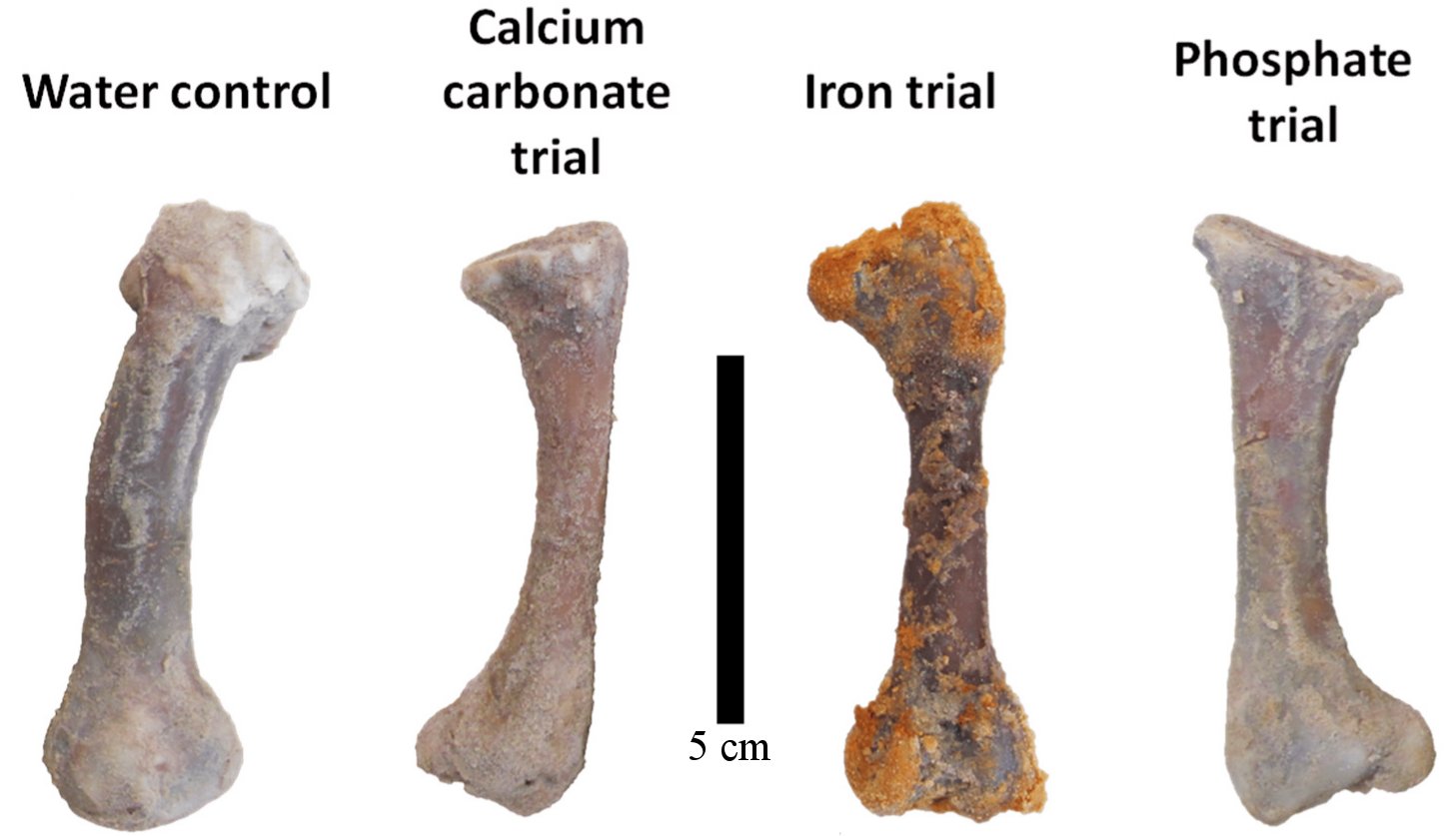
One of my readers (Victor Ferreira da Silva) recently sent me a study that can be considered the death knell of Schweitzer and her colleagues’ proposal. In addition, it strengthens the case that the fossils are not millions of years old. In the study, the authors soaked four chicken femurs in sand to mimic the conditions under which most scientists think fossils form. They then passed a different solution through the sand for each bone: pure water, water + calcium carbonate, water + iron, and water + phosphate. After 90 days, they examined the bones with three different techniques to see how much decay had occurred. They measured the amount of the most abundant form of collagen (a biomolecule) that remained. They found that iron was the worst preservative, and calcium carbonate was the best. Specifically, they estimate that the chicken bones retained 90% of their collagen when exposed to water + calcium carbonate, but only 35% when exposed to water + iron. The ones exposed to water + phosphate retained 60%, while the ones exposed to pure water retained 80%. Under realistic conditions, then, iron is a horrible preservative for biomolecules.
But what about calcium carbonate? When mixed with water, it preserved more collagen. That’s true, and the authors suggest that it’s because the calcium carbonate mineralizes the outer parts of the bone, protecting the inner parts from microbial activity that tends to break down biomolecules. While that seems reasonable, notice that in a mere 90 days, even the “best” preservative had already allowed 10% of the collagen to decay. That doesn’t provide much confidence for its ability to act as a preservative for millions of years!
Interestingly enough, even though I think this study is the death knell for Dr. Schweitzer’s proposal that iron can preserve soft tissue and biomolecules over millions of years, she was indirectly involved in the study. As the authors note:
This project would not have been possible without the support of Mary Schweitzer, who graciously opened her “Modern lab” at North Carolina State University to two of us (PVU and KKV) to conduct the ELISA and immunofluorescence assays for this project.
I applaud Dr. Schweitzer and the authors of this study for trying to figure out an explanation for soft tissue and biomolecules in dinosaur fossils. Of course, I think there is a much simpler explanation: the fossils are thousands of years old, not millions of years old. But I look forward to any more studies done on this issue. If I am right, more studies will simply strengthen the young-earth case. If I am wrong, we will discover some new, exciting chemistry.