In a 2003 speech, John Kerry complained about the Bush administration, saying:
Nothing illustrates this administration’s anti-science attitude better than George Bush’s cynical decision to limit research on embryonic stem cells.
During the heat of the “stem cell wars,” this was a common refrain. Life-saving treatments could be produced with embryonic stem cells, and anyone who questioned whether or not it was morally acceptable to destroy one life in order to experiment with saving another was “anti-science.” Never mind that there are stem cells in everyone’s body, commonly called adult stem cells, and those stem cells also have the potential to cure illnesses. Everyone “knew” that using embryonic stem cells would be better.
What’s the difference between embryonic stem cells and adult stems cells? Well, most of the cells in your body have specific tasks. Your skin cells perform one set of tasks, while your muscle cells perform another set of tasks, your liver cells another set of tasks, etc., etc. These cells have all “specialized” so they can perform their tasks efficiently. A stem cell, by contrast, is a cell that hasn’t yet “specialized.” It can develop into many different cells, depending on your body’s needs.
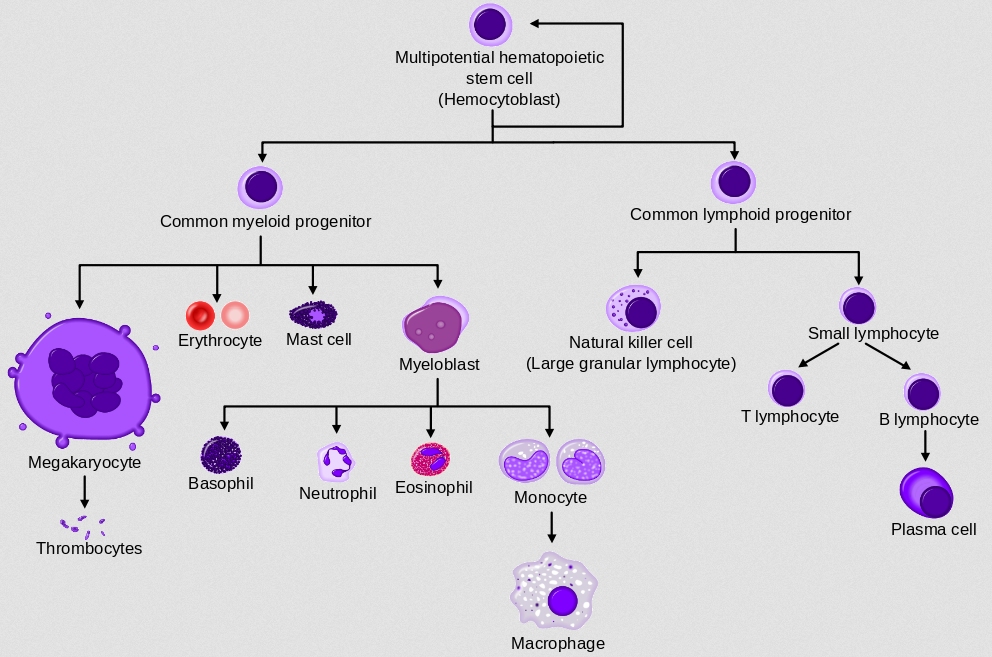
Embryonic stem cells end up developing into all the cells that make up the body, so they are thought to be very, very flexible when it comes to what they can develop into. However, to get those stem cells, you have to kill the embryo. Adult stem cells, on the other hand have already specialized to some degree. For example, the drawing at the top of this post shows how an adult stem cell found in bone marrow can develop into various different blood cells. While that shows some serious flexibility, bone marrow stem cells don’t normally develop into wildly different cells, like skin cells. As a result, it is thought that adult stem cells aren’t as flexible as embryonic stem cells. On the positive side, however, you don’t have to kill anything to get adult stem cells.
Continue reading “Adult Stem Cells Continue to Effectively Treat Illnesses”









